
The older the expectant mother, the higher the probability that the fetus will suffer from Down's syndrome or other diseases.
We offer Post-Pregnancy Prenatal Exam to ensure a safe and comfortable pregnancy.
Although not all abnormalities can be detected, a high probability of detecting congenital diseases can be achieved.
At our clinic, we offer the "Quattro Test" and the "Amniocentesis".
The Quattro Test is a screening test used to calculate the probability of Down’s Syndrome, 18 Trisomy, and open neural tube malformations by measuring the four components that come out of the placenta and fetus in the blood of pregnant women.
As the age of pregnant women increases, so does the probability of children being born with 18 Trisomy and Down’s Syndrome.
From the pregnant woman, we will take a small amount of blood and measure the four components (AFP, hCG, uE3, Inhibin A) that are found within.
These are the components produced by the placenta or the fetus during pregnancy.
The value of these components will fluctuate as the pregnancy progresses, but will also increase and decrease by the fetus being subject to the disease of the examination.
To the value of the these four components, pregnant woman’s age, gestational age, adding in the Japanese reference value, whether or not the fetus has a disease, we will calculate the probability of each and every pregnant woman.
As for the Quattro Test, since it is calculated on the probability of each pregnant woman on the basis of specific probability, there is a tendency that the higher the age of the pregnant woman the higher probability of the results of the Quattro Test.
| Cost | ¥25,000(With Tax: ¥27,500) |
|---|---|
| Exam period | 15-17th week of pregnancy |
| Danger of exam | No harm because it’s a blood test |
*Prices are subject to change without notice.
*Appointment is necessary. Please ask by phone.
You can see the probability of the target diseases (Down’s Syndrome, 18 Trisomy, Open Neural Tube Malformation) that the fetus is at stake for.
For example if the probability is 1/500, and if you had 500 pregnant women with the same probability of 1/500 we can interpret that one of them is pregnant with a child of the target disease.
In a survey of about 20,000cases, there was a positive results of about 9% and among that group about 2% having Down’s Syndrome.
There are 46 chromosomes usually present in humans.
Oocytes and sperm have 22 single autosomes and 1 sex chromosomes making 23‐to‐46 present at fertilization, but in rare cases the chromosome number will be more or less than the norm which will lead to chromosomal anomalies thus resulting in fetus abnormalities.
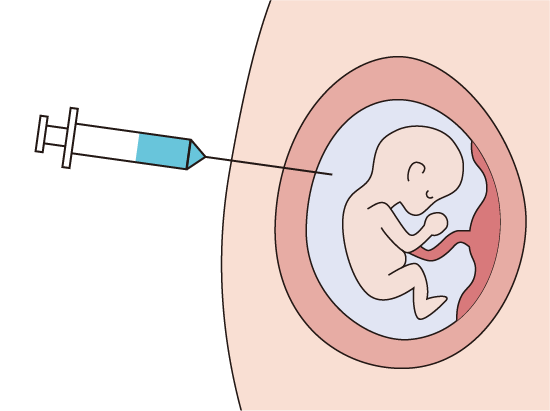
Using fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, amniocentesis (amniotic fluid test) will examine whether there are chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus or not.
General amniocentesis uses G band analysis.
By collecting and culturing fetal cells in amniotic fluid, the chromosomal forms can be identified, stained, and then observed and analyzed.
This method tells us how many chromosomes 1-22 and how many X and Y chromosomes are present in each chromosome.
Using method, we will understand the chromosome pairs 1‐22, and the sex chromosomes X and Y.
Furthermore, since the chromosomes are observed one by one, we can see large anomalous partial amount or translocations (chromosome has been replaced in part).
Unlike the Quattro test, to determine the probability of a particular disease, this result is a definitive diagnosis, but it will not be able to diagnose all types of chromosomal abnormalities.
G band is not able to see the finer abnormalities in the analysis, because there are those small chromosomal abnormalities of microdeletion or nucleotide sequences that are the causes of congenital disease.
Such congenital abnormalities have been called "Chromosome micro deletion syndrome".
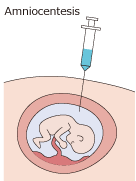 |
Collect amniotic fluid |
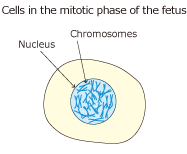 |
Incubate fetal cells in amniotic fluid and dye mitotic cells to locate chromosomes in the nucleus. |
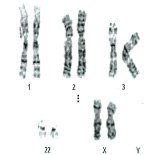 |
Observe the dyed chromosomes under a microscope to identify how many chromosomes there are. Large deletions or surpluses can be seen. |
Chromosome micro deletion syndrome has different symptoms depending on the site of the defect (Table 1), and it is quite common to have no symptoms, but it may merge into severe symptoms.
One famous example isthe DiGeorge Syndrome which has malformation of development, abnormalitiesin heart, mentalretardation accompanied by language disorder and immune deficiency, and the frequency is said to be at 1 in 4,000-5,000 people.
A more accurate analysis method is needed to diagnose this syndrome.
Table 1. Chromosome Micro Deletion Syndromes
| Name | Deleted Chromosome | Main Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Wolf‐Hirschhorn Syndrome | Short arm of chromosome 4 (4p) | Characteristic facial appearance, growth disorders, severe mental retardation, Hypotonia, intractable epilepsy, eating disorders |
| Williams Syndrome | Long arm of chromosome 7 (7q11.23) | Aortic valve stenosis, mental retardation, fairy‐like facial appearance, transient Hypercalcemia in infancy |
| Prader ‐ Willi Syndrome | Long arm of chromosome 15 from father (15q11) | Decreased muscle tone from the time of birth, obesity, Hypogonadism, small hands and feet, mental retardation |
| Angelman Syndrome | Long arm of chromosome 15 from mother (15q11) | Seizures, puppet‐like ataxia, sudden laughter, flapping the hands, severe mental retardation |
| Miller‐Dieker Syndrome | Short arm of chromosome 17 (17p13.3) | Lissencephaly, low upturned nose, severe growth retardation, Seizures, severe mental retardation |
| DiGeorge Syndrome | Long arm of chromosome 22 (22q11.21) | Hypoplasia or absence of the thymus and parathyroid, Heart malformations, cleft palate, mental retardation, psychiatric problems |
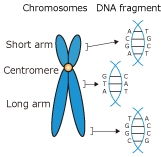
Chromosomes are made up of protein and DNA.
The DNA is bound by a double spiral to 4 kinds of bases; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), and the way the bases are arranged (base sequence) is the genetic information.
The number and sequence of bases has been determined by the species, but about one in several hundred to 1,000 has a part that has a different sequence to the standard base sequence.
The difference of 1 base is called a "snip" (Single Nucleotide polymorphism; SNP), it has become a product of individual differences and diversity.
In the case of humans, it is said that there is “a snip” of about 10 million places in the 3 billion bases, snip related to congenital diseases have also been identified more.
"SNP microarray" analyzes the base sequence of the chromosome, so we can diagnose abnormal micro chromosomes that con not be recognized by G‐band analysis.
 |
 |
 |
||
| Amplify DNA fragments ↓ Hybridization ↓ Analysis |
Even minute abnormalities can be determined. |
This is usually taken around the 17th week of pregnancy from 17weeks 0days - 3days.
For the appointment, a diagnosis of the exact number of weeks (due date) and number of fetuses will be necessary.
It will be done in this order.
Make an appointment after you get the explanation.
Please turn in the consent form at the time of the procedure. (If you forget, we cannot do the procedure).
Check the position of the fetus and placenta with ultrasound, and then disinfect the skin surface of the abdomen receiving the injection needle, and then collect the amniotic fluid 20 ~ 30ml located around the fetus.
In this case, sometimes accompanied by pain and cervical tension, you may use a local anesthetic, if necessary.
Generally it is done from 13:00pm on weekday.
G band analysis and SNP microarray will be done at a professional laboratory.
The results should be ready in 2-3weeks due to the time necessary for the cells to be cultured.
Please come in and get the results explained to you by one of our doctors.
Additionally, if needed, you can receive genetic counseling from our geneticist.
| G‐band analysis (including amniocentesis procedure fee) |
¥169,000(With Tax: ¥185,900) |
|---|---|
| G‐band analysis + SNP microarray (including amniocentesis procedure fee) |
¥269,000(With Tax: ¥295,900) |
*Amniocentesis is not covered by insurance.
*Prices are subject to change without notice.
*Appointment is necessary. Please ask by phone.
English Help Desk
TEL:070-1820-0909
Email:english_help@oakclinic-group.com
[Reception time]
Monday-Sunday 09:00-17:00