
As for the tests that are used for PGD, there is a test to diagnose chromosomes and a test to diagnose genes.
| Testing method | Target | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
aCGH method (array CGH) ,
FISH method |
chromosomes | Habitual miscarriage prevention |
| PCR method | genes | Genetic disease prevention |
This is the latest testing method of preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
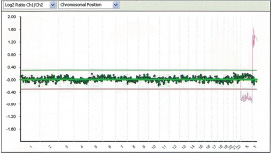
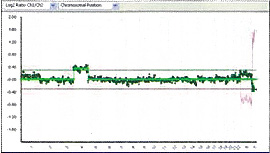
As for the chromosomes, it can check all of the 22 pairs of regular chromosomes and the 2 pairs of sex chromosomes that make up the 24 chromosomes.
It can test the anomalies of the number of chromosomes of trisomies and structural anomalies of imbalanced translocations.
The DNA sample derived from the embryo is compared with a control DNA sample and abnormalities will be detected.
First, the embryo-derived DNA will be amplified by a method called, WGA (Whole Genome Amplification), and then a label will be attached by a red colored fluorochrome.
Additionally for normal DNA samples, a label will be attached by a green colored fluorochrome.
These 2 DNA samples will undergo hybridization reaction with an analysis tool that is called the DNA array*1, and then read by a fluorescent scanner.
If normal, there will be an equal amount of coloring of the 2 DNA samples, and a yellow neutral color will be emitted.
However, if there is aneuploidy, due to the fact the amount of DNA will be different the color emitted will tend to be red or green.
The ratio of this fluorescent intensity is quantified and through graphing the anomalies, the chromosomes will be verified.
*1 Generally, those are fixed arranged to a known detecting DNA foundation of several squared centimeters.
Anver Kulviev, Svetlana Rechitsky and Oleg Verlinsky : ATLAS OF PREIMPLANTATION GENETIC DIAGNOSIS THIRD EDITION : CRC Press
The percentage rate that one can get an accurate diagnosis by aCGH method is 97% and over.
However, due to such errors that may come about by the DNA amplification process that is carried out before the testing procedure, the results becoming complex being unreadable, and therefore cannot be used.
With the FISH method, a specific region of a chromosome can be tested, and the structural anomalies of chromosomes and the number of anomalies can be detected.
The probe (DNA fragment) attached to fluorochrome joined only to the DNA array of specific chromosomes intended will be allowed to undergo hybridization with the cells derived from the embryo, and then by fluorescent microscope the position of the chromosomes with labels attached will be confirmed and anomalies will be identified.
By the FISH method only a maximum of 12 kinds of chromosomes can be tested and thus the aCGH method has become the testing mainstream.
Anver Kulviev, Svetlana Rechitsky and Oleg Verlinsky : ATLAS OF PREIMPLANTATION GENETIC DIAGNOSIS THIRD EDITION : CRC Press
This is a test that can diagnose hereditary disease. The nucleus from one cell of an embryo is taken out, its DNA is amplified, and test for whether or not there is a special hereditary disease.
As for this test, it is used for the diagnosis of single hereditary diseases including dominant and recessive disorders, and because even infinitesimal amount of DNA can be amplified, the PCR method is also used in paternity testing and criminal investigations.
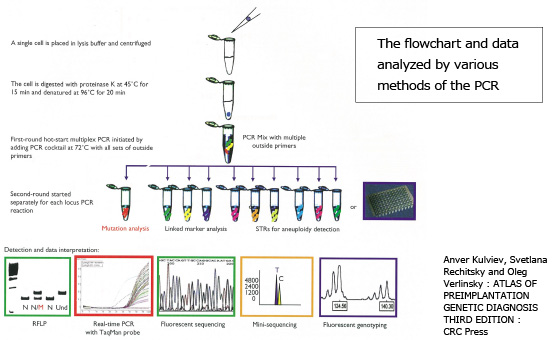
It is possible for the screening of all chromosomes and decision of the genotype.
It differs to aCGH, in that there is no need for sample DNA for comparison nor hybridization, and it will be done only by inspected DNA.
It can detect chromosomal structural anomalies with no copied number changes that cause uniparental disomies, and others such as anomalies of the number of chromosomes and structural anomalies of imbalanced translocations.
The development of DNA sequencing equipment has advanced, and from this a different sequencing technology has come about.
Due to this, the analysis processing capacity has significantly improved, and it has come to be able to get a highly credible test result in a short time.
When using a recent Next Generation Sequencer, it is now possible to decipher the 3 billion base pairs of the human genome that would have taken the old equipment several years to do.
We are providing the general information about Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis.