
Falloposcopic Tuboplasty(FT) is a treatment performed when there is an obvious obstruction or narrowing of the fallopian tubes or other passage obstruction.
In addition to blockage of the fallopian tubes, other causes may include dysfunction of the fine folds in the fallopian tubes, endometriosis/chlamydia, or a congenital condition.
Also, one fallopian tube may be obstructed, making fertilization difficult.
After tubaloscopic Fallopian tube angioplasty (FT), IVF is recommended if general infertility treatment such as timing and artificial insemination does not result in pregnancy after three or more cycles.
It is said that about 30% of infertility is caused by tubal factors.
Fallopian tube angioplasty (FT) is a treatment performed when hysterosalpingogram (HSG) shows obvious obstruction or narrowing of the fallopian tubes or other passage obstruction.
If there is a fallopian tube passage obstruction, the egg cannot meet the sperm and fertilization is not possi.
The idea that there are two fallopian tubes, one of which has an obstruction, but one of which is passing, so it is okay, is also a big mistake.
Although it is generally believed that they ovulate alternately, some ovulate continuously from the right ovary, while others ovulate continuously from the left ovary.
Therefore, if ovulation occurs only from the ovary on the side of the fallopian tube where there is a blockage, fertilization often does not occur.
It is also possible that one of the fallopian tubes is not in good condition, even if one of the tubes passes through. The fallopian tubes have fine folds, and the egg is carried by the movement of these folds.
If this function is weakened, the egg may not be transported properly, making fertilization difficult.
Causes of obstruction range from congenital to endometriosis and chlamydia.
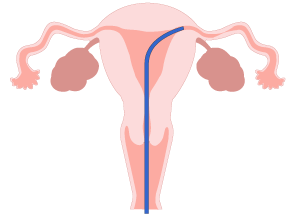
Fallopian tube tube angioplasty (FT) restores tubal sparing and allows direct observation of the condition of the fallopian tubes through a fallopianoscope.
However, since the fallopian tubes are less than 1 mm thick, tubal spacing may not be restored after fallopian tube-specific fallopian tube angioplasty (FT) (about 5%), or may become blocked or narrowed again (about 10%) even after restoration.
The treatment is performed using an instrument with a built-in balloon called an FT catheter of approximately 1 mm and a falloposcope attached to the tip of the catheter.
The catheter is inserted through the vagina into the uterus, and the fallopian tubes are widened with a balloon built into the catheter.
At this time, the spacing of the blocked or narrowed fallopian tubes is restored.
In addition, the fallopian tubes can be directly observed with a fallopianoscope to determine the condition of the fallopian tubes.
Since the surgery can be somewhat painful, we use intravenous anesthesia in our clinic.
The procedure takes about 20 minutes for one side and 30-40 minutes for both sides, and is a day surgery.
(1) A thin tube called an FT catheter is inserted into the uterus through the vagina, and the entrance to the fallopian tubes is checked with a falloposcope (endoscope).
(2) The balloon of the catheter is extended to the blocked fallopian tube, and the narrowed or obstructed area is dilated with the balloon.
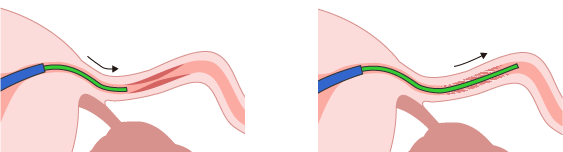
(3) The fallopian tube speculum is placed in the center of the balloon.
After opening the site of obstructed passage, the luminal surface of the fallopian tube is observed as the balloon is pulled back.
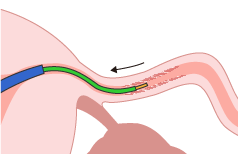
Strong adhesions associated with surgery or other procedures may cause perforation.
In such cases, treatment is temporarily stopped and the patient is monitored with antibiotics.
Usually, symptoms such as intra-abdominal bleeding do not occur, and the condition improves with rest alone.
There is a possibility of abdominal pain, bleeding, and infection after surgery.
Anesthesia may cause allergies and mood disorders.
Fallopianoscopy tubal angioplasty is performed between the end of menstruation and ovulation.
Contraception is required during menstruation until the day after the date of surgery.
If a woman does not conceive after three general infertility treatments using either the timing method or artificial insemination after tubal tubeoscopic Fallopian tube (FT) surgery, IVF is recommended since the problem is thought to be in the fallopian tubes.
(Depending on the results of the observation of the fallopian tubes with a fallopianoscope, we may recommend an early step up to IVF.)
In addition, painkillers are available upon request in case of lower abdominal pain after surgery.
| FT on one side | ¥145,000 |
| FT both sides | ¥280,000 |
*The above amounts are based on 30% health insurance coverage.
*If there is no blockage, the full amount will be paid out-of-pocket.
*If covered by insurance, the high-cost medical care reimbursement system will be applied.
*Prices are subject to change without notice.