
Before insurance coverage, each medical facility could set its own prices. This resulted in significant differences in cost between clinics, sometimes exceeding ¥200,000 for the same treatment.
→ Now that fertility treatments are covered by insurance, each procedure has a standardized fee under the national insurance system. This has eliminated price differences between clinics.
| 例1 | Example 1: 7 Eggs Retrieved, IVF, 3 Blastocysts Frozen Egg Retrieval: ¥26,100 + IVF: ¥9,600 + Fresh Sperm Fee: ¥3,000 + Embryo Culture: ¥32,700 + Embryo Freezing: ¥21,000 = Total: ¥92,400 |
| 例2 | Example 2: 10 Eggs Retrieved, ICSI, 6 Blastocysts Frozen Egg Retrieval: ¥31,200 + ICSI: ¥35,400 + Fresh Sperm Fee: ¥3,000 + Embryo Culture: ¥40,500 + Embryo Freezing: ¥30,600 = Total: ¥140,700 |
| 例3 | Example 3: 2 Eggs Retrieved, ICSI, 1 Early-Stage Embryo Frozen Egg Retrieval: ¥20,400 + ICSI: ¥17,400 + Fresh Sperm Fee: ¥3,000 + Embryo Culture: ¥18,000 + Embryo Freezing: ¥15,000 = Total: ¥73,800 |
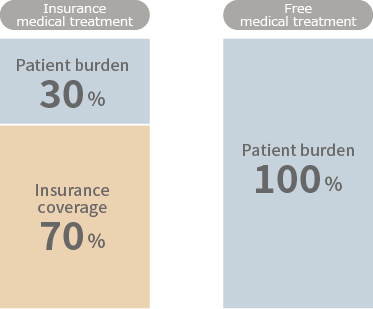
Although the timing of billing varied between medical facilities, patients were typically charged the full 100% of the treatment cost.
→With insurance coverage now in place, patients are generally responsible for only 30% of the total treatment cost.
Fertility treatments have been rapidly evolving, with new specialized techniques and culture media continually emerging.
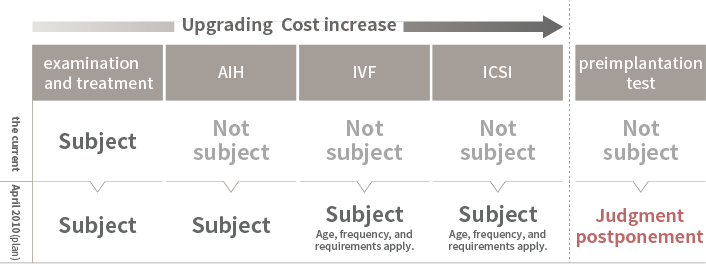
Until now, medical facilities would carefully evaluate and select which technologies and culture media to use, often incorporating specialized techniques as optional additions to existing treatments.
→With the introduction of insurance coverage, approved techniques can now be performed under insurance. However, techniques that have not yet been approved must still be offered as self-paid treatments.
という形で治療を行うことができます。
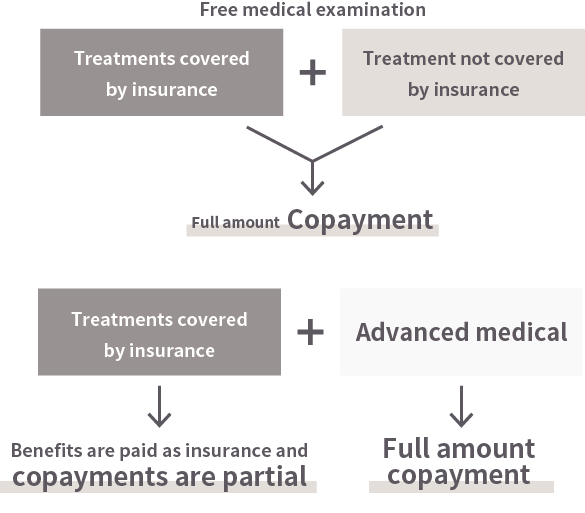
翻訳文章:However, mixed billing combining self-paid and insurance-covered treatments is not permitted. Therefore, if treatment includes any techniques not covered by insurance, the entire process must be conducted as self-paid treatment.
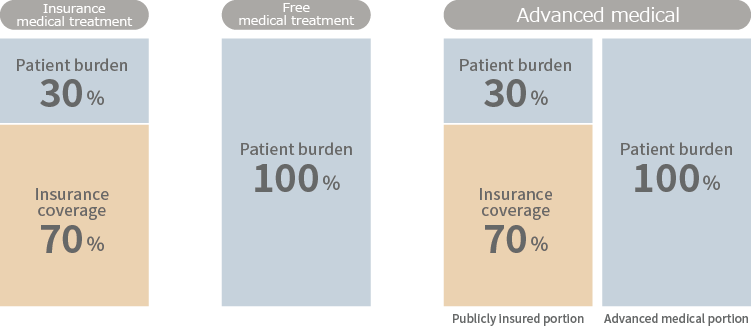
Some advanced medical technologies and tests, while not covered by insurance, are recognized as advanced medical care. In such cases, treatment can be provided as a combination of insurance-covered care and advanced medical care.
Until now, subsidies have been provided by the national government and local municipalities; however, following the introduction of insurance coverage for fertility treatments, these subsidies are scheduled to be phased out after a grace period.
→While the inclusion of artificial insemination—previously not covered by subsidies—under insurance coverage is a significant benefit, some patients will continue to undergo egg retrieval through self-paid treatment. Additionally, in certain cases, patients who had embryo transfers before insurance coverage began experienced lower out-of-pocket costs.
(Figure 1) When Only National Subsidy Programs Are Used

(Figure 2) When Combined with Local Government Subsidy Programs

(Figure 3) Scope of Subsidy Coverage
Techniques not currently covered by insurance but expected to be included in the future can be performed as advanced medical care.
Each technique has specific indications, and if these criteria are met, advanced medical care can be provided alongside insurance-covered treatments.
If you have supplemental insurance with advanced medical care coverage, you may be reimbursed for these costs.
| Types of Advanced Medical Care | Name of Applied Technology | Name of Advanced Medical Technology | Indication | Technology overview | Cost (JPY, tax-exempt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced medical A | PICSI | Physiological Sperm Selection Technique Using Hyaluronic Acid | Infertility (limited to cases of tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or general infertility treatments that have been ineffective, specifically for patients who have repeatedly failed to achieve implantation or pregnancy). | A technique that selects mature sperm using a medium containing hyaluronic acid. | ¥27,500 |
| Time lapse | Fertilized Egg and Embryo Culture Using Time-Lapse Imaging | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective). | A technology that uses a built-in camera inside the incubator to automatically capture images of embryos at regular intervals during culture, enabling accurate embryo assessment without removing them from the incubator. | ¥29,500 | |
| Intrauterine Microbiome Testing (EMMA/ALICE) |
Intrauterine Microbiome Test | Suspected Chronic Endometritis | A test that determines whether the bacterial flora in the uterus is normal or abnormal, and identifies the composition of bacterial species present. | ¥59,850 | |
| SEET method | Endometrial Stimulation | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective). | A technique in which embryo culture medium is infused into the uterus a few days before embryo transfer to create an environment conducive to embryo implantation. | ¥48,300 | |
| Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA) | Endometrial Receptivity Test | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective, specifically for patients who have repeatedly failed to achieve implantation or pregnancy). | A test that collects endometrial tissue and analyzes gene expression using next-generation sequencing to assess whether the endometrium is in a state suitable for implantation. | ¥123,880 | |
| Endometrial Scratch | Endometrial Scraping | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective, specifically for patients who have repeatedly failed to achieve implantation or pregnancy). | A technique in which an endometrial scratch (local endometrial injury) is performed in the cycle before the planned embryo transfer, followed by embryo transfer in the subsequent cycle. | ¥17,540 | |
| IMSI | Morphological Sperm Selection Technique Using High-Magnification Microscopy | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective). | A technique that selects mature sperm using a high-magnification microscope. | ¥48,500 | |
| Two-Stage Embryo Transfer Method | Two-Stage Embryo Transfer Procedure | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective, specifically for patients who have repeatedly failed to achieve implantation or pregnancy, and only those who have undergone endometrial stimulation). | A technique where an early-stage embryo is transferred first, followed by the transfer of a separately cultured blastocyst at a later date. | Fresh Embryo: ¥50,000 Thawed Embryo: ¥70,000 The second stage of the embryo transfer is covered by insurance. |
|
| POC-NGS Test | Genetic Testing Using Miscarriage Tissue Samples | For individuals experiencing a second or subsequent miscarriage, or who have been diagnosed with stillbirth. | This test checks for chromosomal abnormalities in products of conception. Analysis is possible if DNA can be extracted from the tissue. Depending on preservation conditions, the test can also be performed on naturally expelled samples. | ¥100,000 | |
| ZyMot (Sperm Separator) | Physiological Sperm Selection Technique Using Membrane Structure | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective). | A technique that selects mature sperm using a special membrane structure (sperm selection device ZyMot). | ¥33,000 | |
| Intrauterine Flora Test | Intrauterine Microbiome Test 2 | Infertility (limited to tubal infertility, male infertility, functional infertility, or cases where general infertility treatments have been ineffective), suspected chronic endometritis, or refractory bacterial vaginosis. | A test that measures the proportion of Lactobacillus bacteria present in the uterus. | ¥42,860 | |
| Neo-Self Antibody Test |
Anti-Neo-Self β2 Glycoprotein I Complex Antibody Test |
Recurrent pregnancy loss (for those who have experienced two or more miscarriages, excluding chemical pregnancies). | The frequency of neo-self antibody positivity is high among women with recurrent pregnancy loss, suggesting a possible link between neo-self antibodies and recurrent miscarriage. This test measures the antibody levels in the blood. |
¥39,780 |
※From January 1, 2024, fees for advanced medical care will be charged tax-exempt.
*Status of advanced medical care in infertility treatment (as of May 1, 2020)
※From “Overview of Advanced Medical Care” (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
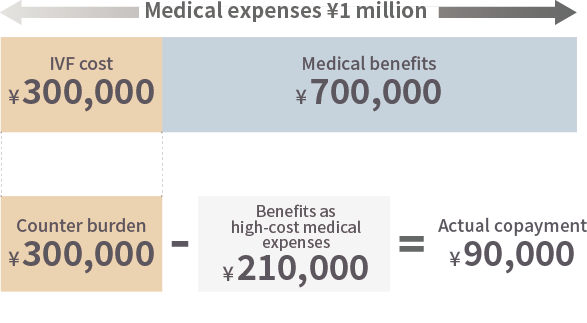
Even though it became covered by insurance, the out-of-pocket amount still exceeds 100,000 yen and is not a small expense.
The High-Cost Medical Expense Benefit System can be used for treatment.
Please make your payment once at our hospital’s reception, then apply for a refund yourself, or before starting treatment, apply to your health insurance society or similar organization for the issuance of a “Certificate of Eligibility” (Certificate of Application for the Maximum Amount).
If you submit the Certificate of Eligibility at our hospital reception, your payment at the counter will be limited to a fixed amount.
However, claims must be made within the same month, and the maximum limit varies depending on factors such as annual income, so please contact your health insurance society or relevant organization for details.
※From “For Everyone Using the High-Cost Medical Expense Benefit System” (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
| Monthly remuneration | Out-of-pocket maximum limit | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle (up to 3 months) | Frequent use (from 4th month onward) | |
| Low-income individuals (exempt from municipal resident tax) |
¥35,400 | ¥24,600 |
| Up to ¥269,999 | ¥57,600 | ¥44,400 |
| ¥270,000 to ¥514,999 | ¥80,100 +(Medical expenses - ¥267,000)×1% |
¥44,400 |
| ¥515,000 to ¥819,999 | ¥167,400 +(Medical expenses -558,000円)×1% |
¥93,000 |
| ¥820,000 and above | ¥252,600 +(Medical expenses - 842,000円)×1% |
¥140,100 |